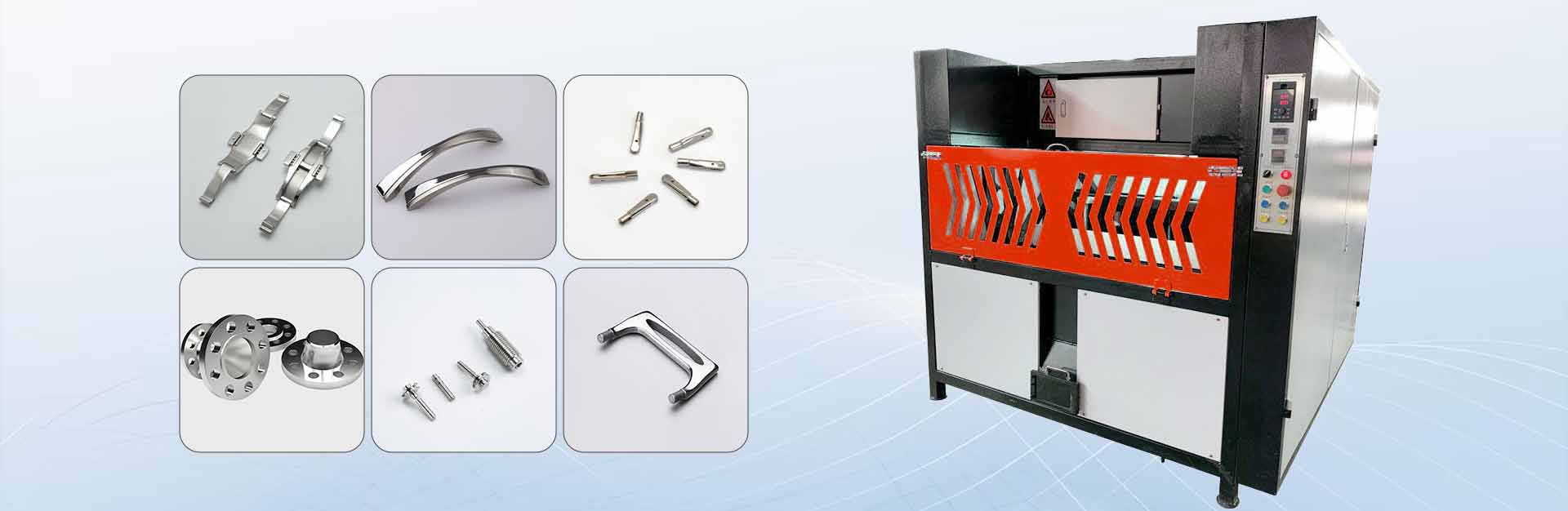

Plastic buffing plays a crucial role in achieving smooth, polished surfaces for various applications. The choice of method depends heavily on the type of plastic and its unique properties. For instance, acrylic and polycarbonate are popular due to their durability and transparency, making them ideal for items like display cases and car headlights. Other materials, such as polyethylene and PVC, require specific techniques to enhance their appearance and functionality. Understanding these differences ensures the best results, whether the goal is a high-gloss finish or a refined edge.
Key Takeaways
- Pick the right buffing method for the plastic type. Use polishing for acrylic and polycarbonate. Flame treatment works well for thermoplastics.
- Think about the finish you want. Polishing gives a shiny surface. Flame treatment smooths edges fast. Chemical polishing is great for detailed designs.
- Check your budget first. Polishing tools can be costly. Flame treatment is cheaper. Chemical polishing costs more because of dangerous materials.
- Know your skill level. Polishing and flame treatment need practice to do well. Chemical polishing is safer for experts because of safety risks.
- Ask a professional for tricky projects. Experts help keep things safe and give better results, especially for valuable or detailed designs.
Polishing
How Polishing Works?
Mechanical Buffing with Abrasives
Polishing involves mechanical buffing to achieve a smooth and refined surface. Abrasives play a crucial role in this process by removing imperfections and creating a polished finish. Common abrasives include plastic-based materials like crushed urea, polyester, or acrylic. These abrasives are available in various hardness levels and sizes, making them suitable for different applications. For instance, they are widely used in industries such as automotive, aviation, and electronics to clean molds or polish plastic parts without damaging the substrate.
Buffing, a traditional method, uses a cotton cloth to abrade the surface. This technique works effectively on all plastics, delivering a smooth surface with limited clarity. For more advanced needs, optical machining and vapor polishing are alternatives. Optical machining provides true optical finishes, while vapor polishing is ideal for clear plastics, ensuring transparency.
Tools and Equipment for Plastic Polishing
The polishing process requires specific tools and equipment to achieve the desired results. Buffing wheels, polishing compounds, and plastic buffing machines are essential for effective polishing methods. Plastic buffing machines offer precision and efficiency, especially for large-scale projects. These tools help remove scratches and enhance the appearance of polished plastic surfaces.
Best Applications
Smooth, Glossy Finishes on Flat Surfaces
Polishing is highly effective for creating smooth and glossy finishes on flat surfaces. This makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring a polished finish, such as display cases, tabletops, and signage. The process enhances the visual appeal and functionality of these items.
Ideal for Materials Like Acrylic and Polycarbonate
Acrylic and polycarbonate are among the most commonly polished plastics. These materials benefit from polishing due to their transparency and durability. In industries like automotive, polishing improves the appearance of car parts, such as trim and chrome components, by providing a mirror-like finish. Similarly, in consumer goods, polished plastic surfaces enhance the aesthetics of kitchen appliances while offering practical benefits like ease of cleaning.
Pros and Cons
Pros: Precise Control, High-Quality Finish
Polishing offers precise control over the process, allowing users to achieve a high-quality finish. It is versatile and works well for various plastics, including intricate designs and flat surfaces. The ability to remove scratches and enhance clarity makes it a reliable choice for many applications.
Cons: Time-Intensive, Requires Skill and Equipment
Despite its advantages, polishing can be time-intensive. Achieving a polished finish often requires skill and experience, especially when working with complex shapes. Additionally, the need for specialized equipment, such as plastic buffing machines, may increase costs for smaller projects.
Flame Treatment
How Flame Treatment Works?
Using a Flame to Smooth Plastic Surfaces
Flame polishing uses a controlled flame to smooth and refine plastic surfaces. The heat from the flame melts the outermost layer of the plastic, which eliminates minor scratches and imperfections. This process creates a glossy and polished finish. Operators typically use a propane or hydrogen torch for this method. The flame must be applied evenly and quickly to avoid overheating or warping the material. Flame polishing works best on thermoplastics like acrylic, which respond well to heat.
Safety and Equipment Considerations
Safety plays a critical role in flame polishing. Operators should wear protective gear, including heat-resistant gloves and safety goggles. Proper ventilation is essential to prevent inhaling fumes released during the process. A steady hand and experience are necessary to control the flame effectively. Beginners may benefit from practicing on scrap materials before attempting to polish finished products. While flame polishing requires minimal equipment, using a plastic buffing machine for pre-polishing can enhance results.
Best Applications
Polishing Edges of Thermoplastics Like Acrylic

Flame polishing is ideal for refining the edges of thermoplastics, particularly acrylic. It smooths rough cuts and sharp edges, making it a popular choice for items like display cases, signage, and aquariums. The process enhances both the appearance and safety of these products.
Quick Touch-Ups for Simple Shapes
This method excels at quick touch-ups on simple shapes. It provides a fast and efficient way to improve the finish of small or straightforward designs. Flame polishing is often used in prototyping and small-scale projects where speed is a priority.
Pros and Cons
Pros: Fast, Effective, Minimal Equipment Needed
Flame polishing offers several advantages. It delivers fast results, making it suitable for projects with tight deadlines. The process requires minimal equipment, which reduces costs. Additionally, it effectively produces a high-gloss finish on compatible plastics.
Cons: Requires Skill, Not Suitable for All Plastics
Despite its benefits, flame polishing has limitations. It demands a high level of skill to avoid damaging the material. The technique is not suitable for all plastics, as some may burn or deform under heat. For intricate designs or materials incompatible with heat, alternative methods like chemical polishing may be more appropriate.
Chemical Polishing
How Chemical Polishing Works?
Using Chemical Solutions to Dissolve Imperfections
Chemical polishing involves the use of chemical solutions to smooth and refine plastic surfaces. These solutions dissolve surface imperfections, creating a uniform and reflective finish. Commonly used solutions include citric acid and nitric acid. These chemicals etch and level the surface by removing roughness and contaminants. The process typically begins with cleaning the plastic part to ensure no debris interferes with the polishing process. Submerging the part in the solution allows the chemicals to work effectively, enhancing the surface texture and achieving a high-gloss finish.
Safety Precautions and Common Chemicals
Safety is critical when handling chemicals during the polishing process. Operators should wear protective gear, including safety glasses, gloves, and dust masks, to prevent exposure to harmful substances. Proper ventilation is essential to avoid inhaling fumes generated during the process. Additionally, handling and disposing of chemicals must follow industry standards to prevent environmental damage and skin burns. Citric acid and nitric acid are widely used due to their effectiveness, but they require careful handling to ensure safety.
Best Applications
Intricate Shapes and Hard-to-Reach Areas
Chemical polishing excels in refining intricate shapes and hard-to-reach areas. This method is ideal for complex designs where traditional techniques like vapor polishing may struggle to deliver consistent results. The ability to polish multiple parts simultaneously makes it a cost-effective choice for intricate workpieces.
High-Gloss Finishes for Complex Designs
This method is highly efficient for achieving high-gloss finishes on complex designs. It provides an ultraclean surface finish, improving both the appearance and durability of polished plastic components. The process also enhances localized corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, extending the service life of the material.
Pros and Cons
Pros: Excellent for Complex Designs, Uniform Finish
Chemical polishing offers several advantages. It allows for the polishing of complex-shaped workpieces without requiring specialized fixtures or power sources. The process is highly efficient, enabling the simultaneous treatment of multiple parts. It also delivers a uniform finish, ensuring a consistent appearance across all surfaces. Additionally, it improves the mechanical properties of the material, making it more durable.
Cons: Hazardous Chemicals, Specialized Equipment Needed
Despite its benefits, chemical polishing has drawbacks. The use of hazardous chemicals poses safety risks, requiring strict adherence to safety protocols. Specialized equipment may also be necessary for handling and applying the chemicals effectively. These factors can increase costs and limit accessibility for smaller projects.
Comparison of Plastic Polishing Methods
Key Factors
Cost
The cost of plastic polishing methods varies significantly. Polishing often requires specialized tools like buffing wheels, polishing compounds, and a plastic buffing machine. These tools can increase expenses, especially for large-scale projects. Flame treatment, on the other hand, involves minimal equipment, making it a budget-friendly option for smaller tasks. Chemical polishing tends to be the most expensive due to the need for hazardous chemicals and specialized safety equipment.
Speed
Speed plays a crucial role in selecting a method. Flame treatment is the fastest option, delivering results in minutes for simple shapes and edges. Polishing takes more time, especially for intricate designs or large surfaces, as it involves multiple steps. Chemical polishing falls in between, offering efficiency for complex shapes but requiring time for chemical application and safety precautions.
Finish Quality
Each method produces a distinct finish. Polishing achieves a smooth, glossy surface with precise control, making it ideal for high-quality results. Flame treatment creates a polished edge or surface but may lack the uniformity of other methods. Chemical polishing excels in delivering a uniform, high-gloss finish, especially for intricate designs and hard-to-reach areas.
Material Compatibility
Material compatibility determines the effectiveness of each method. Polishing works well with durable plastics like acrylic and polycarbonate. Flame treatment is suitable for thermoplastics, particularly acrylic, but may damage heat-sensitive materials. Chemical polishing is versatile, handling complex shapes and various plastics, though it requires careful chemical selection to avoid material degradation.
Side-by-Side Comparison
Polishing vs. Flame Treatment vs. Chemical Polishing
| Factor | Polishing | Flame Treatment | Chemical Polishing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low | High |
| Speed | Moderate | Fast | Moderate |
| Finish Quality | High-gloss, precise | Glossy but less uniform | Uniform, high-gloss |
| Material Compatibility | Acrylic, polycarbonate | Thermoplastics like acrylic | Various plastics, complex shapes |
Polishing offers precise control and a high-quality finish but requires more time and equipment. Flame treatment provides quick results with minimal tools, making it ideal for simple tasks. Chemical polishing stands out for intricate designs and uniform finishes but involves higher costs and safety considerations.
Choosing the Right Plastic Buffing Method
Factors to Consider
Material Type
The type of plastic plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate buffing method. For instance, acrylic and polycarbonate are ideal for polishing due to their durability and transparency. Flame treatment works best on thermoplastics like acrylic, while chemical polishing suits intricate designs made from materials such as polyethersulfone or COC/COP. Selecting the right method ensures compatibility and prevents damage to the material.
Desired Finish
The desired finish significantly influences the choice of method. Polishing provides a smooth, glossy surface, making it suitable for applications requiring high-quality aesthetics. Flame treatment delivers a clear, polished edge but may lack uniformity. Chemical polishing excels in achieving a uniform, high-gloss finish, especially for complex shapes. Understanding the finish requirements helps in selecting the most effective technique.
Budget
Budget constraints often dictate the choice of method. Polishing may require tools like a plastic buffing machine, which increases costs for large-scale projects. Flame treatment is more cost-effective, requiring minimal equipment. Chemical polishing, while efficient for intricate designs, involves higher expenses due to the use of hazardous chemicals and specialized safety gear.
Skill Level
Skill level is another critical factor. Polishing demands precision and experience to achieve optimal results. Flame treatment requires a steady hand to avoid overheating or warping the material. Chemical polishing involves handling hazardous substances, making it more suitable for professionals. Assessing skill level ensures safety and effectiveness during the process.
Decision-Making Guide
Matching Methods to Specific Needs

Matching the buffing method to specific project needs ensures the best results. For example, polishing is ideal for flat surfaces and transparent plastics like acrylic. Flame treatment works well for quick touch-ups on simple shapes. Chemical polishing is the go-to method for intricate designs and hard-to-reach areas. The table below summarizes the suitability of each method:
| Polishing Method | Description | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Buffing | A traditional method using a cotton cloth for a smooth surface. | Works on all plastics. |
| Flame Polishing | Uses a hot flame for an extremely clear surface. | Limited to select materials. |
| Optical Machining | Utilizes special tooling for true optical finishes. | Best for fine finishes. |
| Vapor Polishing | Produces optimal results for clear plastics. | Best for see-through applications. |
When to Consult a Professional?
Certain challenges, such as incorrect material selection or inadequate post-processing, may hinder achieving the desired finish. Consulting a professional becomes essential in these cases. Professionals possess the expertise and equipment, such as a plastic buffing machine, to handle complex projects. Seeking expert advice ensures safety and optimal results, especially for high-value or intricate designs.
Conclusion
Selecting the best plastic buffing method depends on the material type, desired finish, and specific application. Each method—polishing, flame treatment, or chemical polishing—offers unique advantages and limitations. Evaluating these factors helps in making an informed decision. For example, polishing works well for flat surfaces, while flame treatment suits quick edge refinements. Chemical polishing excels in intricate designs but requires careful handling.
Tip: Using tools like a plastic buffing machine can enhance precision and efficiency for polishing tasks.
When in doubt, consulting a professional ensures safety and optimal results, especially for complex or high-value projects.
